O-Zone Therapy
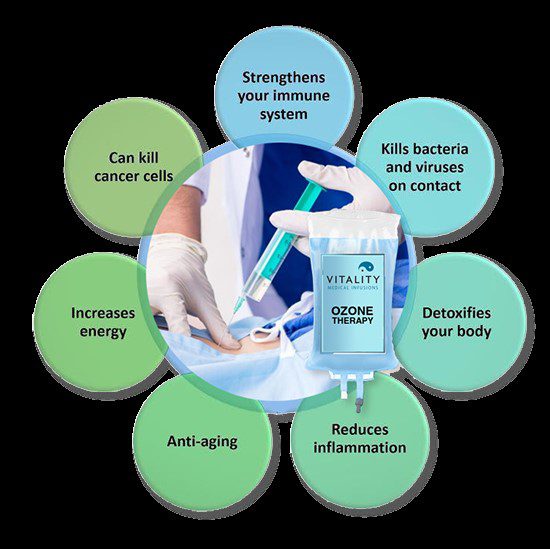
Ozone therapy is a form of alternative medical treatment that involves the administration of ozone gas into the body for therapeutic purposes. Ozone (O3) is a highly reactive form of oxygen that consists of three oxygen atoms bonded together. It can be used in various ways, such as through injection, infusion, or topical application.
While there are claims about the benefits of ozone therapy, it’s important to note that the scientific evidence supporting its effectiveness is limited and controversial. The use of ozone therapy is not widely accepted or endorsed by mainstream medical organizations.
That being said, proponents of ozone therapy suggest several potential benefits, including:
Improved oxygenation: Ozone is believed to enhance the delivery of oxygen to the body’s tissues by increasing the release of oxygen from hemoglobin. This, in turn, may improve cellular function and metabolism.
Enhanced immune system function: Ozone therapy may stimulate the immune system, leading to increased production of white blood cells and improved immune response against infections.
Antioxidant properties: Ozone has been claimed to possess antioxidant effects, helping to reduce oxidative stress and neutralize harmful free radicals in the body.
Anti-inflammatory effects: It is suggested that ozone therapy can reduce inflammation by modulating the release of inflammatory mediators and promoting tissue repair.
Improved circulation: Ozone therapy may enhance blood flow by dilating blood vessels, which could potentially benefit conditions such as peripheral vascular disease.
It’s important to note that the effectiveness and safety of ozone therapy are still subjects of debate and ongoing research. Some medical professionals express concerns about potential risks and side effects associated with ozone therapy, including lung irritation, oxidative damage, and the formation of toxic byproducts.
If you are considering ozone therapy, it is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional who can provide you with accurate information and guidance based on your specific health needs and conditions. They can help you weigh the potential benefits against the risks and explore evidence-based treatment options.
